The Rise of Home Education in the UK
Home education, also known as elective home education (EHE), has experienced significant growth in the United Kingdom in recent years. This trend reflects a broader shift in educational preferences, with an increasing number of families opting to educate their children outside the traditional school system. Recent data indicates a substantial increase in the number of children being home-educated in England. According to the Department for Education, as of the autumn term 2024, local authorities reported 111,700 children in elective home education, marking a 21.4% increase from the previous year. Over the course of the 2023/24 academic year, an estimated 153,300 children were home-educated at some point, up from 126,100 in the 2022/23 academic year (Department for Education, 2024).
Home Education in Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland presents a unique context for home education within the UK. The number of children registered for home education has also risen in recent years, although precise figures are more difficult to obtain due to differences in record-keeping across local councils. According to recent Department of Education statistics, there were approximately 3,100 home-educated children in Northern Ireland in 2024, up from 2,400 in 2020, representing a 29% increase over four years (Department of Education Northern Ireland, 2024). Home education in this region is regulated by law, with parents required to provide a “suitable education” and local authorities empowered to investigate where concerns arise. Despite the regulatory framework, many families report limited formal support from authorities, meaning home-educating parents often rely on peer networks and community groups for resources and guidance (Home Education Network Northern Ireland, 2023).
Reasons for Choosing Home Education
Families choose home education for a variety of reasons, often influenced by individual circumstances and values. Some of the most commonly reported motivations include:
- Mental Health Concerns: A significant number of parents cite mental health issues as a primary reason for opting out of the traditional school system. In the autumn term of 2024, 14% of parents in England reported mental health as the main reason for home education (Department for Education, 2024).
- Philosophical or Lifestyle Preferences: Approximately 14% of families choose home education due to philosophical beliefs or lifestyle choices, seeking an educational experience that aligns more closely with their values and priorities.
- Special Educational Needs (SEN): Children with special educational needs may not receive adequate support in mainstream schools, prompting parents to consider home education as a more suitable alternative.
- Dissatisfaction with the School Environment: Issues such as bullying, rigid curricula, and concerns about safety can lead families to withdraw their children from traditional schools.
- Flexibility and Personalised Learning: Home education allows families to tailor learning experiences to a child’s individual needs, interests, and pace, which can be particularly beneficial for gifted students or those with specific learning requirements
Potential Drawbacks of Home Education
While home education offers numerous advantages, it also presents several challenges that families must consider:
1. Financial Implications: Home education can be financially demanding. Parents are responsible for all educational expenses, including resources, materials, extracurricular activities, and examination fees. This financial burden can be particularly challenging for families with limited income or those who must reduce working hours to facilitate home education (Home-Ed.info, 2023).
2. Socialisation Opportunities: One of the most frequently cited concerns about home education is the potential lack of socialisation. Traditional schools provide children with regular interaction with peers, fostering social skills and friendships. Home-educated children may have fewer opportunities for such interactions, which can impact their social development. However, many families address this by participating in co-ops, community groups, and extracurricular activities.
3. Parental Expertise and Time Commitment: Effective home education requires a significant time investment from parents, who must plan and deliver lessons, assess progress and manage administrative tasks. This responsibility can be overwhelming, especially for parents without a background in education. Additionally, balancing home education with other responsibilities can lead to stress and burnout (High Speed Training, 2023).
4. Access to Resources and Support: Home-educated children may have limited access to resources typically available in traditional schools, such as specialised teachers, extracurricular programs and support services. While some local authorities provide support to home-educating families, the level of assistance varies and may not meet all the needs of the child (Department for Education, 2024).
5. Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Home education is legal in the UK, but parents must ensure they comply with certain legal requirements. This includes notifying the local authority of their decision to home-educate and providing an education that is suitable to the child’s age, ability, and aptitude. Failure to meet these requirements can lead to legal challenges and potential intervention by local authorities (Department for Education, 2024).
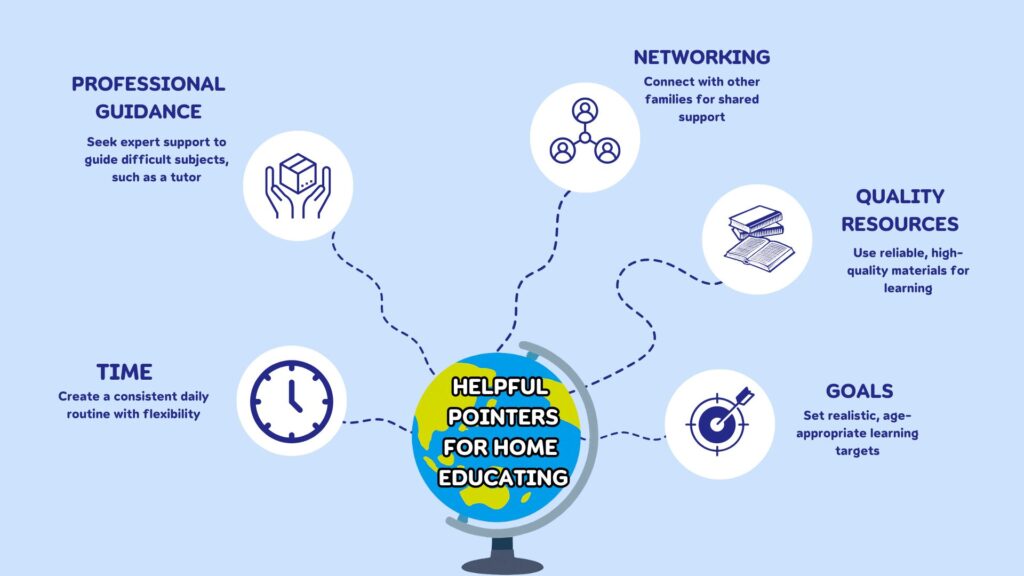
Conclusion
The rise of home education in the UK reflects a growing desire among families for greater control over their children’s education. While this approach offers personalised learning experiences and can address specific concerns, it also comes with challenges that require careful consideration and planning. In Northern Ireland, the increase in home-educated children highlights similar motivations alongside region-specific regulatory and cultural factors. Families contemplating home education should weigh the benefits against the potential drawbacks and seek support and resources to navigate this educational path effectively.

